Introduction: Complications of Exodontia
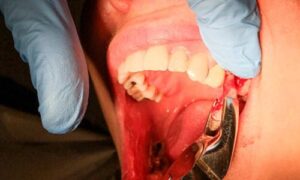
Exodontia, commonly known as tooth extraction, is a routine dental procedure performed for various reasons, including decay, infection, or orthodontic purposes. While most extractions are successful, complications can arise, requiring careful consideration and management by dental professionals. This article will explore the potential complications associated with exodontia and how they can be addressed.
Bleeding:
One of the most common complications following tooth extraction is bleeding. While mild bleeding is normal, excessive or prolonged bleeding can be a cause for concern. Clot disruption, underlying medical conditions, or medication interactions may increase bleeding. Dentists must provide patients with proper postoperative care instructions and monitor them for signs of abnormal bleeding.
Infection: Complications of Exodontia
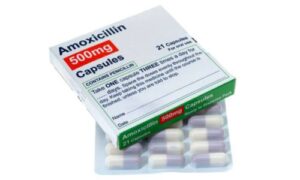
Infections are potential risks associated with any surgical procedure, and exodontia is no exception. Bacterial contamination or improper wound care can lead to infections. Dentists often prescribe antibiotics to mitigate this risk and emphasize the importance of following postoperative care guidelines, including maintaining oral hygiene to reduce the likelihood of infection.
Dry Socket:
Dry socket, or alveolar osteitis, occurs when the blood clot that forms after extraction is dislodged or dissolves prematurely, exposing the underlying bone. This condition can be extremely painful and delay the healing process. Dentists may recommend special dressings and pain management strategies to alleviate discomfort and promote healing. Patients must avoid smoking and vigorous rinsing in the days following extraction to reduce the risk of developing a dry socket. If symptoms of dry socket persist or worsen, it is crucial to seek prompt dental care for proper treatment and management.
Nerve Damage:
In some cases, nerves near the extraction site may sustain damage during the procedure, leading to temporary or, in rare cases, permanent numbness or altered sensation. Dentists take precautions to minimize the risk of nerve damage, such as carefully planning and evaluating the tooth’s position and surrounding structures. If nerve damage does occur, dentists may recommend further evaluation by a specialist to determine the best course of action for treatment. Patients need to communicate any unusual sensations or changes in feeling to their dentist following an extraction.
Fractured Roots or Teeth:
Complex extractions may involve dealing with fractured roots or teeth, posing challenges for complete removal. Dentists must skillfully navigate such situations to prevent leaving behind fragments that could lead to infections or other complications. Dentists may use specialized tools and techniques to safely remove fractured roots or teeth, such as sectioning the tooth or using a surgical handpiece. A referral to an oral surgeon may sometimes be necessary for more complex extractions.
Allergic Reactions:
Some patients may experience allergic reactions to medications, anesthetics, or materials used during the extraction. Dentists should be aware of patients’ medical histories and potential allergies to minimize this risk. Additionally, dentists should have emergency protocols to address any allergic reactions that may occur during or after the extraction procedure. Dental professionals must communicate effectively with patients about potential risks and ensure they are well-informed.
Swelling and Bruising:
Post-extraction swelling and bruising are common, particularly in more complex cases. This is a natural response to trauma, but excessive swelling can impede the healing process. Dentists may recommend applying ice packs and prescribing anti-inflammatory medications to manage swelling and discomfort. Patients should be advised on the duration of expected swelling and when to seek further assistance if it persists.
Sinus Complications:
Extractions of upper molars, especially in the posterior region, can sometimes lead to sinus complications. An opening between the oral cavity and the sinus can occur, causing sinus communication. Dentists must be cautious during such extractions and may advise patients to avoid certain activities, like blowing their nose forcefully, to prevent complications. Patients should also be informed about the signs and symptoms of sinus complications, such as persistent nasal congestion or discharge. If any of these symptoms occur, patients should seek prompt evaluation from their dentist or healthcare provider to prevent further complications.
Postoperative Pain Management:
Pain is a common concern after tooth extraction. Dentists often prescribe pain medications and provide guidelines on their proper use. Non-pharmacological approaches, such as warm saltwater rinses and a soft diet, can also contribute to pain management. Patients should communicate their pain levels to their dentist for appropriate adjustments in medication or treatment.
Delayed Healing:
Compromised immune function, systemic diseases, or poor adherence to postoperative care instructions can lead to delayed healing. Dentists may recommend additional measures, such as nutritional supplements or more frequent follow-up appointments, to monitor and support the healing process in these cases.
Anesthesia Complications:
Complications related to anesthesia can include adverse reactions, allergies, or even systemic issues. Dentists carefully assess patients’ medical histories and choose appropriate anesthetic techniques. Awareness of potential complications allows for quick intervention and proper management to ensure patient safety. Patients should always disclose any allergies or medical conditions to their dentist before anesthesia. This information will help the dentist make informed decisions and minimize the risk of complications during treatment.
Psychological Impact with Complications of Exodontia
The extraction process can have psychological implications for some patients, leading to anxiety or fear of future dental procedures. Dentists should be attuned to patients’ emotional well-being, providing reassurance and, if necessary, referring them to mental health professionals for additional support. Patients’ emotional well-being is important in dental care, as anxiety can impact treatment outcomes. Dentists can help patients feel more comfortable and confident during procedures by addressing psychological concerns.
According to The Journal of the American Dental Association, 21.3% or more than 1 in 5 adults have untreated tooth decay, which can lead to the need for tooth Extraction.
Conclusion: Complications of Exodontia
Exodontia is generally a safe and common dental procedure, but complications can occur. Dental professionals are crucial in preventing, identifying, and managing these complications to ensure optimal patient outcomes. Patients, in turn, must adhere to postoperative care instructions and promptly report any unusual symptoms to their dentist. Careful consideration and appropriate measures can minimize the complications associated with exodontia, allowing for a smoother and more successful recovery process.
Faqs about Complications of Exodontia
Q: Is nerve damage common during tooth extractions?
A: While not common, nerve damage can occur, leading to temporary or, in rare cases, permanent numbness or altered sensation. Dentists take precautions to minimize this risk.
Q: How can infections be prevented after tooth extraction?
A: Infections can be prevented by following proper postoperative care guidelines, including maintaining good oral hygiene and taking any prescribed antibiotics as directed by the dentist.
Q: What should be done if a tooth extraction involves fractured roots or teeth?
A: Dentists must skillfully navigate such situations to ensure the complete removal of fragments, minimizing the risk of infections. In some cases, additional procedures may be required.
Q: Are there any allergic reactions associated with tooth extractions?
A: Some patients may experience allergic reactions to medications, anesthetics, or materials used during the extraction. Dentists should be aware of patients’ medical histories to minimize this risk.
Q: How can patients contribute to a successful recovery after tooth extraction?
A: Patients should adhere to postoperative care instructions provided by the dentist, report any unusual symptoms promptly, and attend follow-up appointments to ensure optimal recovery and healing.
Read More:
Braces, Invisalign, or Clear Aligners: Which Is Right for You?