Dental X-rays are often essential for children to find any problems buried below the gum line and beneath the enamel of the teeth. However, many parents question whether they are safe for their children. Dental X-rays are often essential for children to find any problems buried below the gum line and beneath the enamel of the teeth. However, many parents question whether they are safe for their children. The good news is that dental X-rays are safer than ever, thanks to contemporary technology.
X-rays are electromagnetic radiation that may penetrate human flesh yet are invisible to the naked eye. The density of the tissue determines how much radiation (energy) absorbs, which is how X-ray images (radiographs) produces. For instance, when X-ray energy passes through a cavity, a darker image that may be seen on film or a sensor is created.
Digital X-rays have mostly replaced the outdated film versions in many dental practices. They are less dangerous than film X-rays because they produce around 80% less radiation. The radiation dose from a series of digital X-rays is lower than that humans naturally receive over a day.
When determining whether dental X-rays are essential, a qualified dentist will carefully assess the risks and benefits depending on the kid’s specific needs. Dental X-rays are never administered randomly, especially to young patients, due to the slight possibility that they could result in cancer.
Children are more radiosensitive than adults, and the FDA, which oversees X-ray equipment, acknowledges that parents should be concerned about their children being exposed to X-rays. The FDA mandates that X-ray machines have child-specific settings that minimize radiation exposure.
As Low as Reasonably Achievable (ALARA) is the recommended radiation dosage standard for health practitioners, including dentists. In contemporary dentistry, digital X-ray technology and procedures enable the delivery of deficient radiation levels.
Expert dentists only perform routine X-rays if they adhere to the American Dental Association (ADA) and American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (AAPD) X-ray recommendations. The ADA and AAPD advise against using X-rays before a clinical evaluation of the patient and a review of their medical history. Including any primary X-ray usage and frequency.
Advantages of dental X-rays in children
Although X-rays are diagnostic, they can serve as a preventative tool by assisting in identifying problems in your child’s mouth before they worsen. Without an X-ray, it may be difficult to detect many possible issues with the teeth and surrounding tissue, such as small areas of decay under fillings, bone infections, abscesses, and tumors.
X-rays are also essential for identifying concerns, including jaw and tooth root problems, gum disease, and gingivitis. A successful treatment strategy depends on the early detection of these issues.
Without X-rays, problems that are not immediately noticeable could go untreated, leading to progressive worsening and potentially threatening your child’s overall health. A gum infection can spread to the lungs, heart, and brain if it is not treated and other organs.
Different X-ray kinds
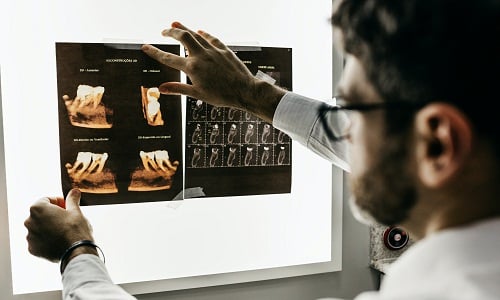
The most popular type of dental radiography, intraoral X-rays, creates images inside the mouth. Your child’s dentist can assess tooth development and root health and see cavities. Examine how securely the jaw bone is anchoring teeth, and identify any possible dental crown needs since they display the precise characteristics of teeth and supporting bones.
X-rays are taken extraoral or beyond the mouth, focusing on the larger skull bones, particularly the lower and upper jaw. These pictures assist your child’s dentist in keeping an eye on the jaw joint’s health and identifying issues like impacted teeth.
The generation of bitewing radiographs is a common application for dental X-rays in children. The word “Bitewings” refers to the tiny tabs or wings affixed to the films or sensors on which the youngster bites. They are essential for detecting decay between the rear teeth, where cavities are frequently hidden from view. Bitewing X-rays are safe, exposing a child to less radiation than they would typically receive from background radiation from the environment regularly.
The dentist for your child can view the entire mouth in one image thanks to Panoramic Radiography.
They are used to evaluate wisdom teeth and the teeth and supporting bone in general. A panoramic X-ray reveals the state of the teeth, including any that have not yet surfaced—the health of the upper and lower jaws, and the tissue and structures surrounding them.
Cephalometric projections from orthodontic X-rays show the whole side of your child’s head. These photos can be beneficial in determining the best course of orthodontic treatment. Straighten up crooked or misaligned teeth because the teeth are shown in the same image as the head and jaw.
When the dentist wants to determine the spacing and growth of the teeth in your child’s mouth, Cone beam computerized tomography (CBCT) X-rays provide them with a three-dimensional perspective.
With your child’s dentist, weigh the benefits and drawbacks.
X-rays are essential in diagnosing teeth and gum problems because they allow for the proper course of action and treatment (such as the requirement for a tooth extraction) before the issue worsens. Professional radiologists can carefully interpret X-rays to identify problems that might go unnoticed.
Most of the time, the information offered by a dental X-ray will result in long-term health advantages for your child that vastly outweigh the hazards of the operation. Many diagnostic procedures can entail some risk.
It would help if you were well-informed about the risks, advantages, and alternatives to decide whether or not your child needs dental X-rays. Ask your dentist to explain how the procedure results would benefit your child’s healthcare. And why another method of diagnosis would be less beneficial if they advise your child to undergo an X-ray. An excellent dentist will be pleased to go through these details with you.
Children with a low risk of tooth decay don’t need X-rays as frequently, so helping your child establish a solid oral hygiene practice at home will lessen the frequency of X-rays.
The Top Reasons Why It’s Critical To Brush Your Teeth Before Bed